
04 Aug The New Age of Digital Assets: Blockchain
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a technology that allows you to create a secure and trustworthy digital data structure among unrelated organizations. Although blockchain technology existed before, it gained popularity when Satoshi Nakamoto published his paper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” in 2008. In this paper, Nakamoto demonstrated how to establish a secure data recording system without the need for central authorities, using blockchain. This technology is one of the technologies that enables us to transition to Web 3.0, which aims to document people’s digital assets.
Blockchain functions like a ledger that encrypts information and records data changes in interconnected blocks. Unlike a centralized ledger controlled by a single authority, the blockchain ledger is locally stored and simultaneously updated on all computers participating in the blockchain network. As a result, no single computer can control or modify the records arbitrarily, making the blockchain an extremely secure data repository.
Why is Blockchain Technology Secure?
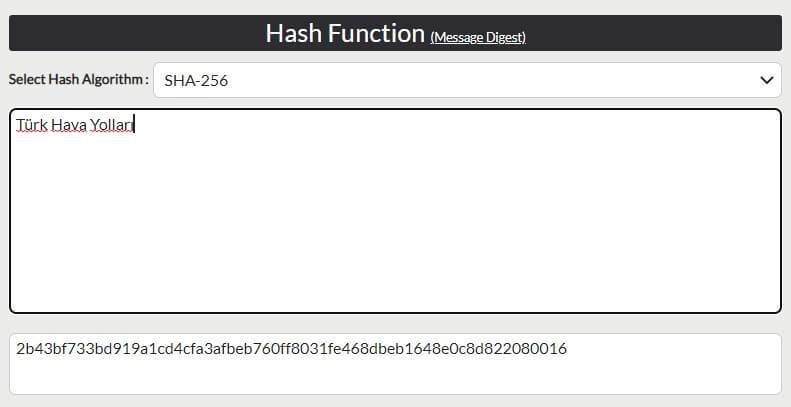
Blockchain encrypts and stores data using mathematical cryptographic functions. For instance, if we input “Turkish Airlines” into the encryption function used by Bitcoin, we would get the output “2b43bf733bd919a1cd4cfa3afbeb760ff8031fe468dbeb1648e0c8d822080016,” a series of numbers and letters. Every change made to the input text creates a new encrypted output. Each block in the blockchain contains the encrypted data of the previous block, creating a chain-like pattern.
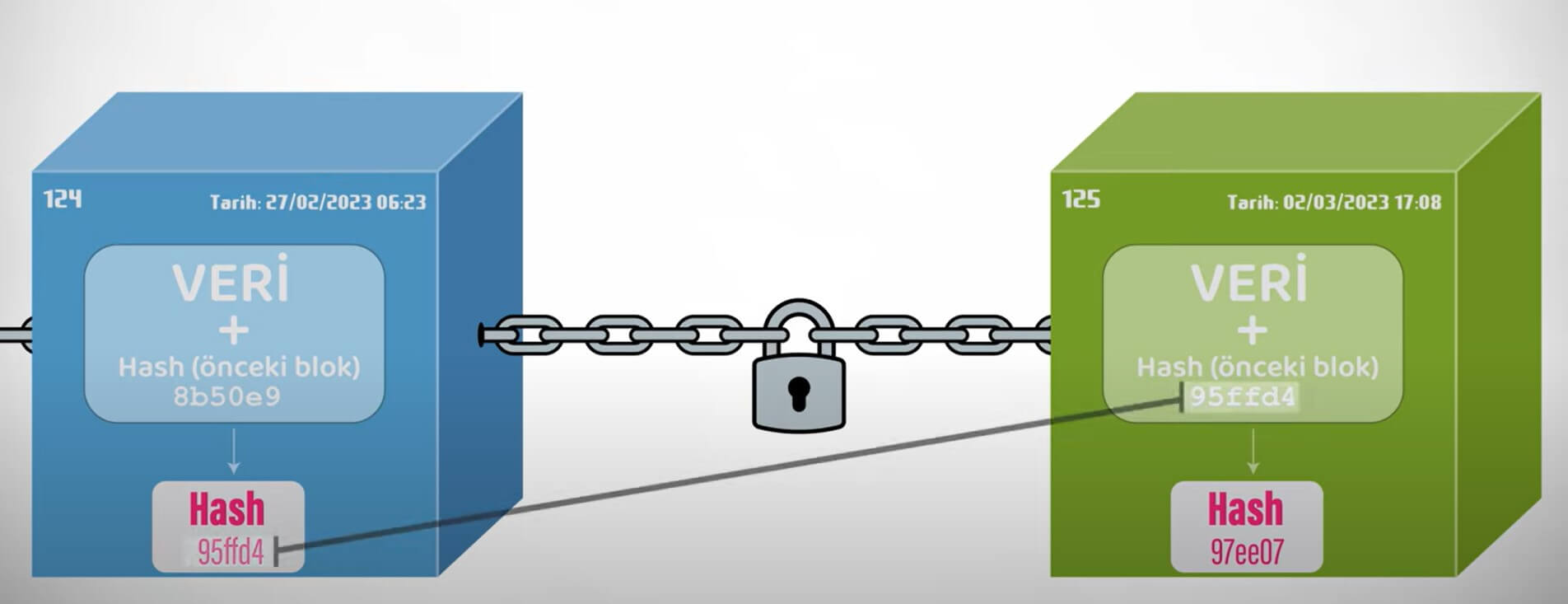
The system in the blockchain called “consensus” allows each block to be added to the end of the chain only after it is simultaneously announced to the entire network and receives approval from all computers. The sequential progress of the blockchain and the principle of consensus make the blockchain network secure.
How can we effectively use the data in the blockchain?
Applications that fully harness the power and security of blockchain technology are smart contracts. These computer programs, capable of processing data on the blockchain, automatically execute transactions when specific conditions are met.
An interesting example of smart contract usage can be demonstrated by AgriDigital, a company that provides smart contract services operating on a blockchain network among farmers, buyers, and suppliers. Through these smart contracts, the delivery of crops and the availability of sufficient funds from the buyer are automatically verified. Once the delivery is confirmed, the sale is executed, and the payment is automatically sent to the stakeholders’ wallets. In short, smart contracts enable secure transactions through blockchain technology without the need for any intermediary.
What are NFTs?
NFTs, also known as “Non-Fungible Tokens,” represent unique digital assets, each of which is one of a kind, indicating ownership of digital items such as artworks, audio recordings, videos, virtual clothing, etc.
Utilify, a service provider in the NFT space and a participant in our Terminal Acceleration Program, offers companies the ability to create NFT campaigns for their customers. Utilify conducts transactions on various blockchains and holds the data. In our “Memory NFT” project created exclusively for the Champions League Final, Utilify automatically generated wallets for the event participants and used a smart contract to transfer the NFTs to the wallets when the “Get Memory NFT” button was pressed. This allowed the participants to own personalized digital memorabilia.

What companies use blockchain technology in travel sector?
Here are the travel sector companies that use blockchain technology:
- Aeron: Offers services on the blockchain for keeping flight records of pilots and matching air traffic control data with pilot records.
- Ozone:Provides an open-source platform that consolidates flight ticket booking, hotel reservation, and car rental services under one roof.
- TravelinBlock: Offers smart contract services that work in connection with tour operators, travel agencies, flight, and hotel providers.
- Trustabit: Provides a solution using blockchain and smart contracts to automatically issue vouchers to airline customers for delayed or canceled flights.
- Loyyal: Enables customer rewards and incentives through a blockchain-based loyalty program created through partnership agreements.
- Winding Tree: Offers a solution to track real-time hotel and flight availability on its created blockchain network.
- Singapore Airlines KrisFlyer: Provides the KrisPay digital wallet service, allowing customers to use earned loyalty program points as a payment method at affiliated establishments.
How can we use this technology as Turkish Airlines?
Here is the compilation of some potential use case scenarios.
- Instead of passengers traveling internationally having to provide separate identity and fingerprint information to each country while acquiring visas, biometric data can be securely stored on a decentralized blockchain network created on behalf of the government by a trusted institution like IATA. By doing so, the participating institutions can verify passengers’ identities without the need for additional information. Technologies capable of achieving such feats already exist today. An example of such a technology is Dfns , a crypto security firm that can authenticate users’ identities using biometric fingerprint and facial data.
- Every airline collects passenger data to better understand their customers. A community of trusted airlines like Star Alliance can utilize blockchain technology to share this data through a common system and collaborate. This way, even the smallest changes in passenger information can be instantly reflected to all authorized entities in real-time. While blockchain technology is already being used in banking, its implementation in the aviation industry is yet to be explored.
- Maintaining a secure record of all service histories of aircraft parts from production until the present on the blockchain will significantly contribute to cost reduction. An example of such a system is the agreement between Air France, KLM ve SkyThread. According to this agreement, a blockchain network is used to store information about an aircraft part, including its lifespan, place of production, certification, added notes, maintenance details, and transfer history. This allows for easy tracking of the part’s journey from production to recycling, even if it is sold.
- Passenger tickets can be issued to passengers as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). This way, tickets can be kept as memorabilia after the flight or sold to others as NFTs before the flight. Flybondi, a low-cost airline, actively uses this system for domestic flights.
- With wider adoption of NFT usage, we can establish an NFT-based marketplace like All Nippon, Etihad, and Airbaltic airlines, where we can organize auctions and offer our customers the opportunity to purchase various digital assets.
- With the use of smart contracts that leverage flight and passenger information, payment parameters, and flight execution status, compensation payments and the provision of meal or hotel vouchers can be automatically processed in cases of flight delays or cancellations. Thanks to a company named Trustabit, there is no need for customers to ask extra questions in compensation situations.
- For our Miles&Smiles members, a blockchain network will be created at airports, and members can earn points from participating stores included in the network. Through smart contracts, the points earned by a person making a purchase can be directly transferred to their account if they are flying with Turkish Airlines and are a Miles&Smiles member on the same day.
- On our blockchain network, which will be established with ground service companies such as TGS and Çelebi, service fee payments can be instantly executed through smart contracts when the services we receive are approved by both Turkish Airlines personnel and responsible ground service employees.
If you have any other potential use scenarios in mind, please share them with us. Let’s evaluate them together in person 🙂
To learn more about blockchain, you can check out the book “Blockchain101 ” by Ahmet Usta and Serkan Doğantekin.
