09 Nov A Modern Journey from Idea to Innovation
In today’s world where everything changes rapidly, technologies, systems, products, habits are consumed in a short time and another one comes to their place in the blink of an eye. It has become even more value-added as a result of generating solutions by centering the feelings and thoughts of human beings, whose essence has not changed, although their needs have changed. This constant change and human orientation made it compulsory to use new and innovative methods.
We would like to share with you the three methods (Lean Startup, Design Thinking and Agile Project Management) used to adapt to this change at the THY Technic Innovation Center (Innaviation Center) and a study example revealed by these methods.
We can briefly explain the prominent features of these methods as follows;
Design Thinking: Design Thinking tries to get to know the user / person with empathy, identifies the primary problems and finds innovative solutions to their hidden needs.
Lean Startup: It takes a solution proposal as a hypothesis, collects feedback quickly with the build-measure-learn cycle, pivot (change the strategy by sticking to the goal) according to the result or protects and improves the solution. The aim is to design a result-oriented product by creating minimum viable products (Minimum Viable Product – MVP) and receiving feedback from the user / customer.
Agile Project Management: Assigns defined tasks to the project team to quickly turn the build-measure-learn cycle, reveals the MVP (product / service) at the end of the cycle and presents it to the customer / user with daily short review meetings.
You can see the relationships and working principles of these three methods in the image below,
Design Thinking-Lean Startup-Agile Methods Working Together
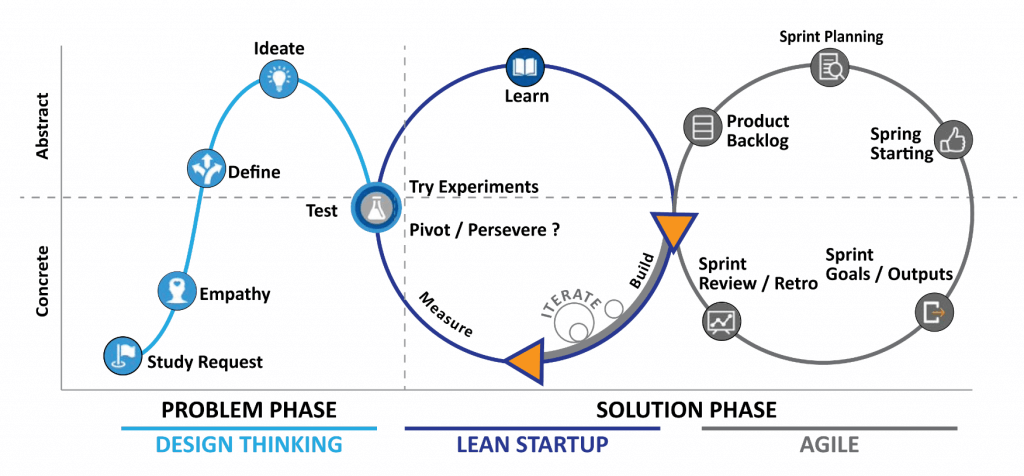
The main steps of dealing with a problem / need with this hybrid methodology can be summarized as follows;
- First of all, it is examined whether the demand from the user/customer is a real need/problem.
- Information is given about the targeted work plan to be presented to the requesting user.
- Value hypothesis and growth hypothesis for the need/problem are determined.
- Understanding persona (Target User/Customer) starts with creating an Empathy Map,
- What they feel, think, do and say is analyzed and recorded,
- If there is a solution method applied to the need, the Story Board is created,
- The story of the targeted experience (Story Board) is written and visualized,
- Solution proposals are prioritized and MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) are aimed to be revealed,
- With the Agile methodology, it is divided into tasks and followed on the Scrum Board,
- Each solution proposal is taken as a hypothesis and tested with the Build-Measure-Learn cycle,
- Whether MVP meets the need is evaluated with the user/customer,
- It is pivoted according to the result or the result is preserved to transform the POC into a sustainable model with the same solution strategy.
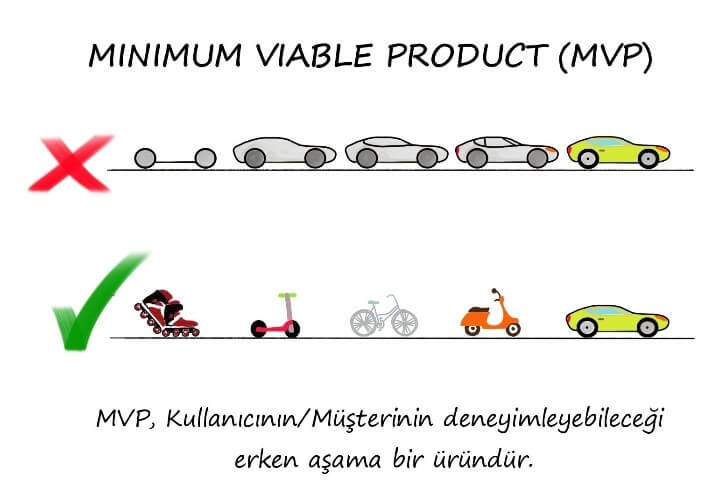
MVP (MINIMUM VIABLE PRODUCT)
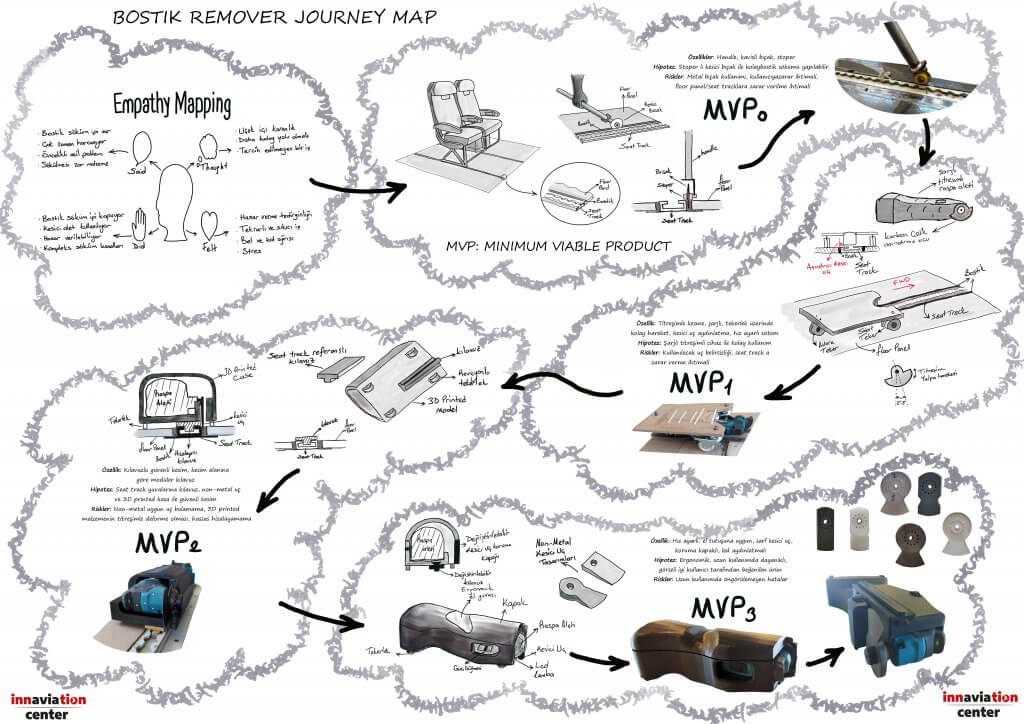
Below are the empathy studies carried out regarding the removal of the bostik material used for sealing between the floor panels and seat tracks encountered in Aircraft Maintenance and the hypotheses at each stage, the experienced problems and their solutions;
Bostik Remover Journey Map You can take a quick look at the journey map (Journey Map) from idea development to POC (Proof of Concept) product, examine the hypotheses and stages tested in each MVP and see the details in the following part of the article.
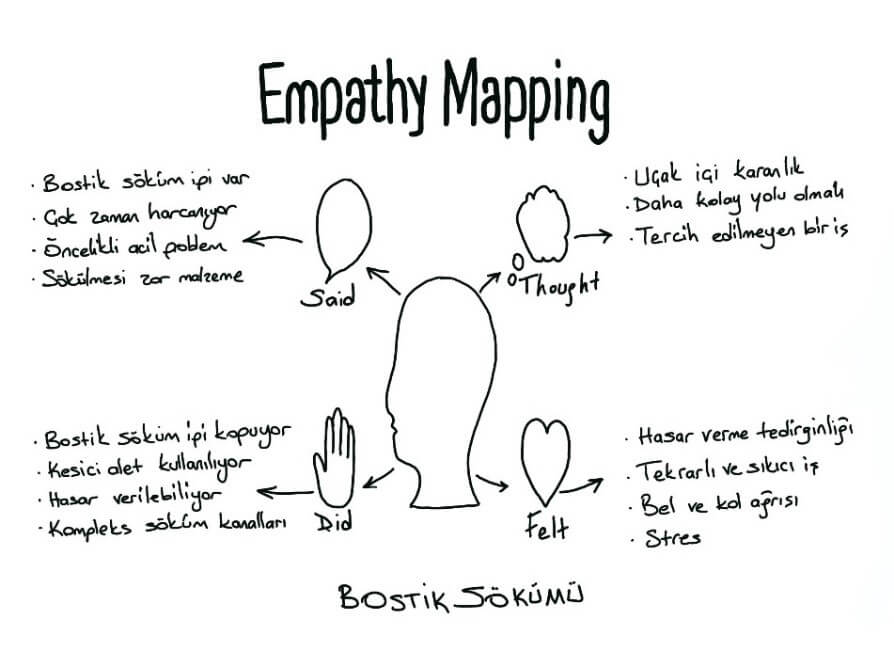
First of all, empathy should be exercised in order to understand the user / customer in depth, to understand the physical and emotional needs of the users, what they use, how they think and what they mean, and as a result to produce the solution that the user needs.
In the empathy phase, the daily lives of the users are observed firstly. Inconsistencies between what users say and what they do are noticed. Focus is on what the user says, thinks, does and feels.
Bilateral meetings are made with users. Questions are asked for users without deviating from the main topic. In order to understand exactly what the users are thinking and doing, it is desirable to repeat the activity with the problem in question, if possible. In the meantime, users should be allowed to think aloud. The information obtained as a result of all these interviews are recorded with Empathy Mapping. You can examine the mapping study on Bostik removal below.
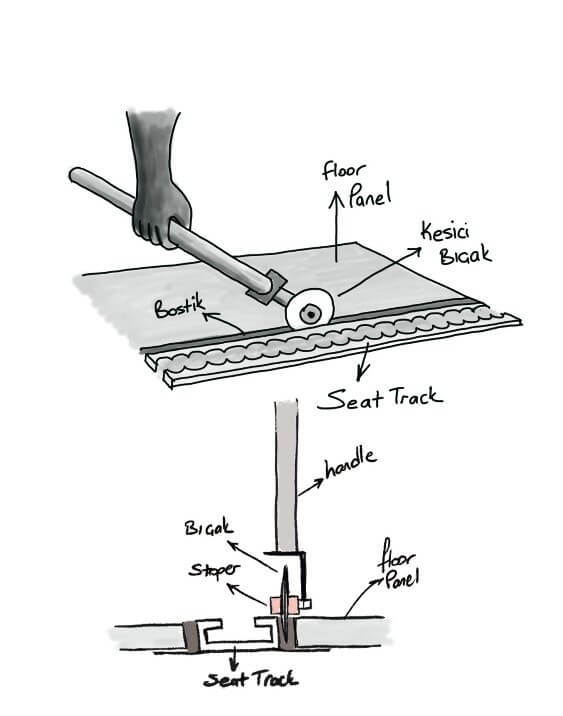
The first developed solution concept MVP0 aimed at effective cutting with metal blade and stopper. A product was quickly developed and tested to test this assumption in the field. Although it seems easy to cut with a metal blade for technicians doing the bostik cutting job; such an extremely sharp metal has the risk of both damaging the worker and creating corrosion caused by a cut on the seat track.
In addition, it was very tiring for the user to continuously advance such a tip in a direction with a certain force. Sharpening the insert at certain times was also a situation that should be considered. It had to pivot, as a solution that could move more easily and was less tiring was needed.
MVP0 Sketch Tasarımı
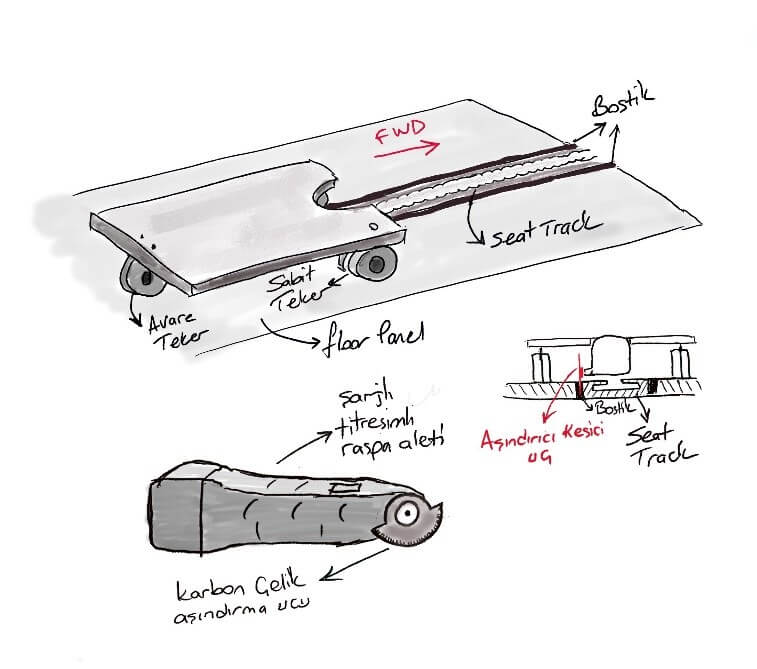
In MVP1, it was focused on a cutting experience that would not tire the user by moving easily in one direction. This solution had to be able to easily cut the bostik material, which hardened over time on the plane. Because there is a considerable difference in hardness between the newly applied bostik and the bostik that has waited in the aircraft for five years. Accordingly, the vibrating scraper tool was considered as a solution. It seems extremely advantageous for continuous cutting that the tool is rechargeable and the spare battery is easily changed. In addition, with a light coupled to the device, it is possible for the user to perform the cutting operation in dark environment in the aircraft. Therefore, in this MVP, the solution was preserved as the hypothesis of a wheeled system that would advance the device linearly was verified in the field. (Persevere)
MVP1 Sketch Tasarımı
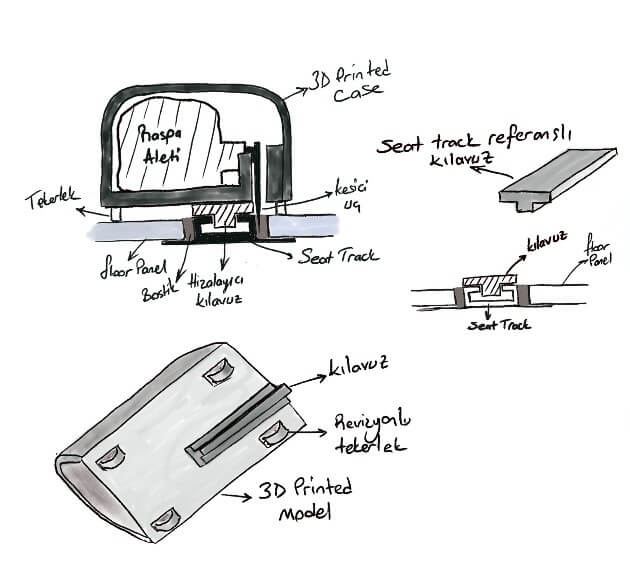
In MVP2, the scraper tool and the guide system that will allow the tool to move in one direction with its lower and upper casing that will carry this tool with a wheeled system was targeted and it was modeled as 3D in computer environment after the sketch design. The said parts were produced and assembled with 3D printers available in the Innovation Center. Placement problems have been dealt with in the issues of very uneven surface form of the scraper tool, the placement of the tool in the case, and the alignment of the insert in the bostik region. Despite this, very positive feedback has been received on cutting and on progress with the tests that are made with the user. This MVP hypothesis was mostly preserved, but despite the high performance of the cutting tip being metallic, the issue of damage to the seat track emerged as another problem to be solved.
MVP2 Sketch Tasarımı
By the time we arrived to MVP3 came, a great distance had been covered. However, the process of cutting meters of bostik strips on each plane easily, while not damaging the seat track, the need to descend to a certain depth during cutting, and the existing bostik applications in the plane in different areas as flat, inclined and ninety degrees and solving all these with a single tool. It was a really tough process. At this stage, ergonomic design revisions were made and insert types were tested.
MVP3 Sketch Tasarımı
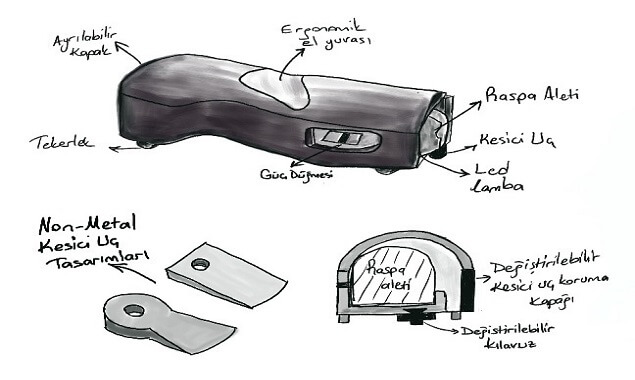
As a result, in the light of all the tests, feedback and experiences, it has become possible to cut effectively without damaging the seat track and without tiring the user with the specially formed insert made of non-metallic material. The insert allows easy replacement and is protected under the protective cover on the case with ergonomic grip.Easy disassembly and replacement of the guide moving in one axis also provides an advantage in working with different bostik thicknesses.
This study, which is achieved with the effective application of these innovative methods and the rapid prototyping facilities in Makerlab in our innovation center, has gained us a value-added experience in the search for solutions in other bostik dismantling/scraping areas on the plane.
In summary, when Design Thinking-Lean Startup-Agile Project Management methods are operated with a do-measure-learn cycle in harmony with each other, a lean, agile, result-oriented and dynamic working structure such as startups emerges and innovation studies from each targeted category (product, process, marketing, organization) can be concluded faster.
